Choosing the Right Pipe Material for Sewer Systems
Discover the best pipe materials for sewer systems with our expert guide. Learn about durability, cost, and suitability for various environments.
Choosing the Right Pipe Material for Sewer Systems
Selecting the appropriate pipe material is crucial for the efficiency and longevity of sewer systems. Various factors such as cost, durability, and environmental conditions play a significant role in this decision. This guide will help sewer inspection professionals make informed choices.
The Importance of Pipe Material Selection
Choosing the right pipe material affects not only the initial installation but also the long-term maintenance and performance of sewer systems. The wrong choice can lead to frequent repairs, increased costs, and environmental hazards.
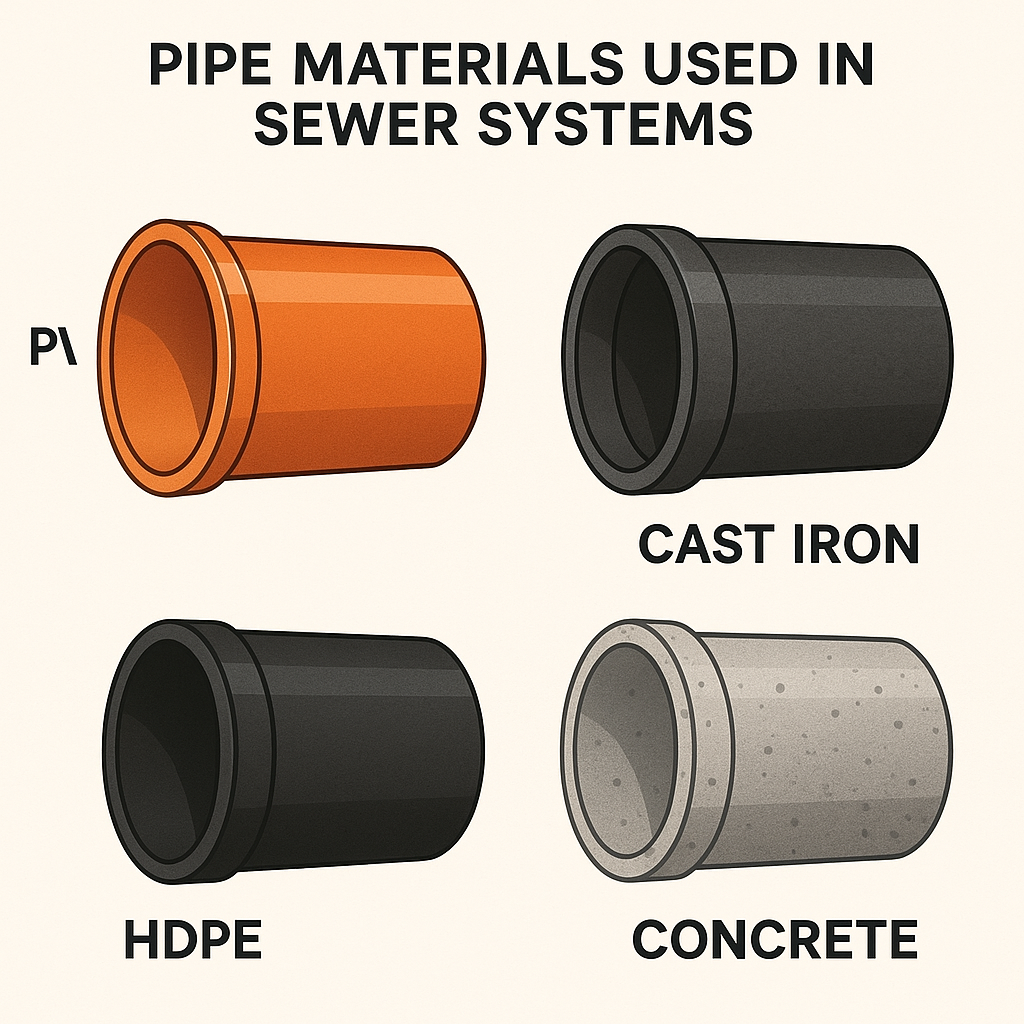
Common Pipe Materials
1. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC pipes are widely used due to their affordability and ease of installation. They are resistant to corrosion and chemical damage, making them suitable for many environments.
Advantages
- Cost-effective: Lower cost compared to metal pipes.
- Corrosion-resistant: Ideal for areas with acidic water.
- Lightweight: Easier to handle during installation.
Disadvantages
- Temperature limitations: Not suitable for high-temperature applications.
- Brittleness: Can become brittle over time, especially in cold environments.
2. Cast Iron
Known for its durability and strength, cast iron is often used in older sewer systems.
Advantages
- Durability: Long lifespan if maintained properly.
- Soundproofing: Excellent at reducing noise from water flow.
Disadvantages
- Heavy: Difficult to install without heavy machinery.
- Corrosion: Prone to rust without proper coating.
3. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
HDPE pipes are known for their flexibility and are often used in trenchless technology.
Advantages
- Flexibility: Can withstand ground movement.
- Resistance: Excellent resistance to corrosion and chemicals.
Disadvantages
- Cost: Generally more expensive than PVC.
- Installation: Requires specialized equipment for joining.
4. Concrete
Concrete pipes are traditional choices for large sewer systems due to their strength.
Advantages
- Strength: Ideal for large-diameter applications.
- Longevity: Long service life.
Disadvantages
- Weight: Extremely heavy, requiring specialized equipment.
- Porosity: Can absorb water, leading to potential cracking.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Pipe Materials
Environmental Conditions
Consider the soil type, water table, and potential chemical exposure.
Cost and Budget
Balance initial installation costs with long-term maintenance and replacement expenses.
Installation and Maintenance
Evaluate the ease of installation and the potential need for future repairs.
Industry Trends
- Sustainability: Increasing focus on eco-friendly materials like recycled plastics.
- Technology: Advances in trenchless installation techniques.
- Regulations: Adherence to local and international standards for sewer systems.
Practical Tips for Sewer Inspection Professionals
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections to identify potential issues early.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure compatibility between different pipe materials to prevent leaks.
- Upgrade Planning: Plan for future upgrades to incorporate new technologies.
Conclusion
Selecting the right pipe material is a critical decision for sewer inspection professionals. By considering factors such as cost, environment, and long-term performance, you can ensure a reliable and efficient sewer system.
FAQs
-
What is the most cost-effective pipe material? PVC is generally the most cost-effective due to its low initial cost and ease of installation.
-
Which material is best for high-temperature applications? For high-temperature sewage, materials like cast iron or specialized metals are recommended.
-
Can different pipe materials be combined? Yes, but it requires careful planning to ensure compatibility and prevent leaks.